With the velocity of risk rapidly changing, what does this mean for those navigating this landscape?
Redhand Advisors and Origami recently released their 2022 reports: the RMIS Report and State of Risk Report, respectively. Robert Petrie, Co-founder & CEO of Origami Risk; James Curbeam, a long time risk management professional, joined me in a recent webinar in which we shared key themes from our reports.
Here are the three current trends in risk management and risk technology we discussed in the webinar:
1. Two classes of RMIS Users have emerged: leaders vs. laggards
Risk managers who actively use RMIS systems get the most out of the technology. This has created two classes of users: leaders and laggards. Leaders are more effective and forward-facing, while laggards are typically not as effective and struggle with using RMIS technology.
Origami’s State of Risk report found leaders use RMIS systems in more innovative ways. The 2022 RMIS Report found similar trends:
- 59% of users thought RMIS technology is very or extremely effective. They think highly of the systems and get more use out of them.
- 41% of users thought RMIS technology is somewhat, slightly, or not effective. These encompass users less comfortable with the technology.
2. Tech use is increasing with RMIS systems
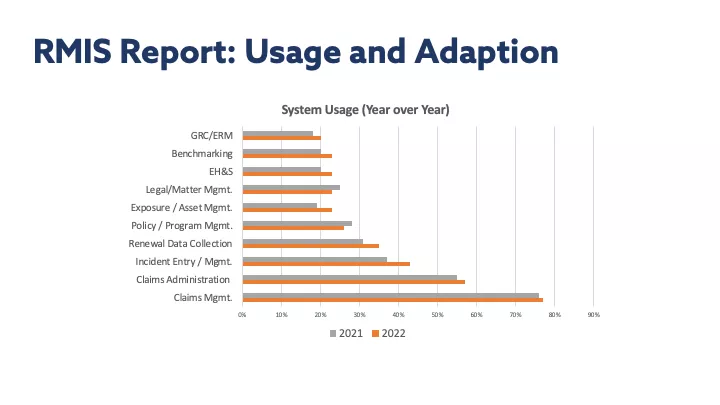
With RMIS technology now offering more options that ever before, businesses are taking advantage of all these systems have to offer. We’re seeing deeper usage and higher adoption of RMIS systems with current users. There is now a 35% usage rate, compared to 31% in 2021 and 28% in 2018.
All features, across the board, are being used significantly more in 2022 vs. 2021. For years, about 70-80% of businesses primarily used a RMIS for claims management. That’s traditionally why people purchased a RMIS. In this year’s report, we’ve seen big jumps in the following categories: benchmarking, exposure and asset management, ERM, EH&S, and incident entry. Incident entry experienced the biggest jump as people started using RMIS software to report and manage COVID cases.
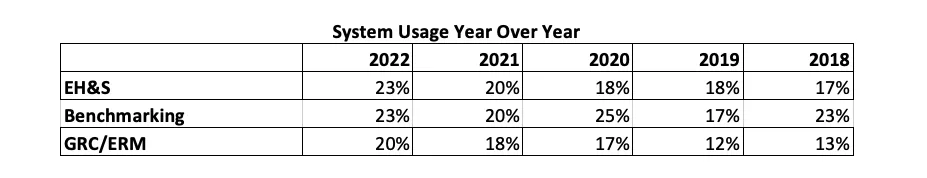
As recently as five years ago, businesses weren’t using RMIS for EH&S and GRC/ERM. Now they’re practically core capabilities, with about 20% or more of RMIS systems used exclusively for these two functions. The following chart shows how far EH&S, GRC/ERM, and benchmarking usage has come:
As usage trends up in all three categories, it is clear the industry is taking a more holistic approach to integrated risk management.
3. Tying management to overall strategy is smart business
In risk management, it is impossible to be strategic without good data and analytical tools. While 43% of leaders have made progress connecting risk with strategic objectives, only 15% of laggards have done so.
Leaders are increasingly thinking about how strategy relies on analysis, and they are taking steps forward to improve capabilities. On the other hand, a large cohort of organizations, the laggards, say this isn’t a priority. They cite financial impacts like costs, investors, fraud, and adapting to change through organizational agility as more pressing concerns. Leaders’ concerns focus more on consumer and employee protection, operational disruption, cyber security and data privacy, regulatory compliance, and brand reputation.
Regardless of whether an organization’s approach to risk management qualifies them as a leader or a laggard, risk tech spending is on the rise in 2022. About 84% of companies are increasing their risk tech spending in 2022, spending on average 8% more on risk tech compared to what Gartner forecasts will be 4% more in IT spending[1] in 2022.
In the next five years, risk tech spending will trend toward mobile at 67%, big data analytics at 59%, and artificial intelligence at 46%. Other risk tech categories include machine learning, robotic process automation, Internet of Things, no-code/low-code solutions, and blockchain.
To learn more about other insights presented in Origami’s inaugural State of Risk report and the 2002 RMIS Report, view the webinar here. For more information on optimizing your RMIS, schedule an inquiry call with Redhand Advisors.
[1] Gartner. “Gartner Forecasts Worldwide IT Spending to Reach $4.4 Trillion in 2022”—April 2022