Insurers find themselves struggling with how to keep up with the pace of technological change. Available cloud solutions that manage core insurance systems break down into three broad cloud categories:
-
On premise: the insurer provides all required infrastructure and network access for an installed platform.
-
Cloud hosted: the software is installed within a cloud provider’s managed environment, but the insurer is responsible for updates, upgrades, and patches.
-
SaaS (software-as-a-service): the software is managed by the software provider who is responsible for updates, upgrades, and patches.
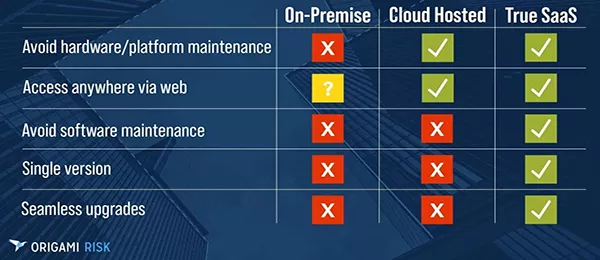
The chart below shows where the software is hosted and how the software is designed and maintained under each of the above three categories This is a critical piece of the cloud puzzle for insurers because it shows which options require insurers to use internal IT resources for installation, maintenance, and support of the software. One of the categories does not require internal insurer IT support.
SaaS platforms do not require insurer IT support for software maintenance. Even with on-premises systems or simple cloud-hosting solutions, insurers know that eventually they will need a major upgrade to their existing systems, requiring downtime and the allocation of a large part of their budget to internal IT resources for the upgrades.
The advantages of SaaS
SaaS platforms are offered on a software subscription basis. From the insurer perspective that means updating, new features, and software maintenance are the responsibility of the SaaS provider. Insurers do not need to worry about it or budget for it.
Another major feature of SaaS platforms is how they are designed. SaaS is designed from the ground up to support multitenancy. That means software development resources are focused on one platform, eliminating compatibility issues, and allowing for economies of scale, thus reducing hosting and IT support costs.
What defines SaaS is not only technological development, but also its ability to offer a working business model for insurers. For example:
-
When software is updated and new features are added, the SaaS provider does all the updating, creating new features, and maintaining the SaaS platform
-
The platform is highly scalable and expands easily.
-
SaaS is accessible from any digital device, smart phone, and at any location.
-
SaaS platforms can be configured to meet basic processes and to push the system beyond the boundaries to address constant change or unforeseen roadblocks easily and quickly.
-
SaaS platforms promote collaboration across teams and departments through file sharing across systems.
-
Known for their enterprise-level security, SaaS platforms emphasizes a comprehensive approach to security, as opposed to on premise and cloud-hosted solutions.
The future of SaaS and insurance
Insurers have gone from being skeptical about cloud computing to embracing ‘cloud-first’ infrastructure strategies, according to Novarica. Based on input from more than 80 insurer CIO members of the Novarica Research Council, key findings of this recent survey report:
-
Insurer use of the cloud moved from 70% to 90% in less than five years.
-
While insurers use cloud computing for storage and compute functions, insurers reported they were also interested in expanding to other areas such as improved security, and access to APIs, data analytics, and AI (artificial intelligence).
-
Half of the insurers interviewed said they saw cloud computing as a net positive on security and cost variability. They also saw total cost and skills required on cloud options such as on premise and cloud hosting as negatives on average.
By reducing the need and expense associated with maintaining systems and upgrading every few years, small-and-medium size insurers can now begin to benefit from the same cost structure and advanced technology used by larger competitors. Advanced technology available through SaaS includes AI (artificial intelligence) machine learning (ML), centralized analytics, vertical SaaS, and API connections (application programming interfaces).
Insurer success is Origami’s central focus
Instead of concentrating resources on maintaining systems, insurers can concentrate on today’s business challenges and future growth opportunities. To learn more about how Origami can help insurers navigate SaaS and transform insurance operations, request a demo here.